How does the 2023 NEC clarify overcurrent protection for legally required standby systems?
Overview
Legally required standby sources are vital for powering critical equipment in facilities such as hospitals, contributing to the safeguarding of public safety. However, earlier versions of the NEC did not provide clear guidance on the wiring and overcurrent protection for these systems. The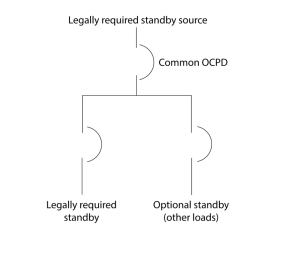 2023 revision of NEC Section 701.10 rectified this by allowing the placement of overcurrent protection devices on feeders serving both legally required and optional loads, with the stipulation that they must be selectively coordinated with all downstream protection devices. This promotes safe and reliable power delivery, along with effective fault clearance and mitigation, which helps to minimize downtime. The 2023 update clarifies the wiring and protection requirements for legally required standby systems.
2023 revision of NEC Section 701.10 rectified this by allowing the placement of overcurrent protection devices on feeders serving both legally required and optional loads, with the stipulation that they must be selectively coordinated with all downstream protection devices. This promotes safe and reliable power delivery, along with effective fault clearance and mitigation, which helps to minimize downtime. The 2023 update clarifies the wiring and protection requirements for legally required standby systems.
Applying the 2023 Code
Legally required standby sources are alternative power sources mandated by laws, codes, or regulatory agencies to supply critical equipment and systems essential for functions like emergency lighting, fire alarms, and communication systems in vital facilities such as hospitals and fire stations, ensuring life and public safety. Ensuring the reliability of these standby systems is paramount, and it must be accomplished through proper wiring to safely deliver power to the required loads of the facilities.
In previous editions of the NEC, the wiring requirements for legally required standby systems were outlined in Section 701.10, permitting wiring through the same raceways, cables, boxes, and cabinets used for general wiring. However, it did not specify the requirements for installing overcurrent protection devices along the wiring. NEC 2023 updated this section to allow for the installation of an overcurrent protection device on single or multiple feeders for the legally required and optional loads, provided it is selectively coordinated with downstream protection devices. This addition provides end users with additional guidance and clarification on their options for installing wiring and overcurrent protection devices for legally required systems.
What’s New for the 2023 NEC?
The table below presents a comparison between the 2020 NEC and the 2023 NEC regarding Section 701.10.
2020 NEC |
2023 NEC |
| 701.10 Wiring Legally Required Standby Systems
The legally required standby system wiring shall be permitted to occupy the same raceways, cables, boxes, and cabinets with other general wiring. |
701.10 Wiring Legally Required Standby Systems
(A) General The legally required standby system wiring shall be permitted to occupy the same raceways, cables, boxes, and cabinets with other general wiring. (B) Wiring Wiring from a legally required source to supply legally required and other (nonlegally required) loads shall be in accordance with the following: 1) The common bus of switchgear, sections of a switchboard, or individual enclosures shall be either of the following: a) Supplied by single or multiple feeders without overcurrent protection at the source b) Supplied by single or multiple feeders with overcurrent protection, provided that the overcurrent protection that is common to a legally required system and any nonlegally required system(s) is selectively coordinated with the next downstream overcurrent protective device in the nonlegally required system(s). |
Login with your site account
Not a member yet? Register now
Register a new account
Are you a member? Login now
